|
INTEGRAL WORLD: EXPLORING THEORIES OF EVERYTHING
An independent forum for a critical discussion of the integral philosophy of Ken Wilber
Publication dates of essays (month/year) can be found under "Essays".
The Human Growth
Continuum
à Tables illustrating the growth continuum page 23 à Resources for study page 40 à Glossary of terms page 43 à Credits page 47 à Biographical background page 48
SPECIAL NOTE For maximum benefit, any Table with an up-arrow should
be read from bottom to top –
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Life cycle step |
Stages/ |
Age of |
Characteristics |
|
25 |
Legacy |
After-death |
Genetic, cultural, psychological & material endowments passed to succeeding generations |
|
24 |
Death |
|
Physical functioning stops |
|
23 |
Senescence |
95-100+ |
Diminished capacities |
|
22 |
Debility or illness |
|
Significant physical or mental setback |
|
21 |
Elderhood |
75-95 |
Communicating experience and wisdom to next generation |
|
20 |
Passing-the-baton |
|
Recognition of mortality. Shift of attention to next generation. |
|
19 |
Mature adulthood |
55-75 |
Shift to internally-validated identity. From success to significance |
|
18 |
Mid-life passage |
|
Breakdown of externally-validated identity |
|
17 |
Middle adulthood |
35-55 |
Stability of stature and position |
|
16 |
Making-the-grade |
|
Peak of external life achievements. |
|
15 |
Young adulthood |
21-35 |
Striving for external life achievements |
|
14 |
Nudged from the nest |
|
Completing school. Finding real job, permanent partner |
|
|
[college] |
18-22 |
Independent identity, while supported by home |
|
13 |
Adolescence |
13-18 |
Formation of independent identity, while living at home |
|
12 |
Coming-of-age |
|
First adolescent traits – physical, psychological |
|
|
[upper grades] |
9-12 |
|
|
11 |
Older childhood |
6-8 |
Early schooling. First enrollment in society outside the home. |
|
10 |
Entering school |
|
First days at school |
|
9 |
Young childhood |
3-6 |
Partial independence within home environment |
|
8 |
Onset of Terrible 2s |
|
First actions independent of mother |
|
7 |
Toddler |
1.5-3 |
Early efforts at self-initiative and self-support |
|
6 |
Crawling/ walking |
|
First mobility |
|
5 |
Infancy |
0-1.5 |
Total sustenance and bonding outside the womb |
|
4 |
Birth |
|
Emergence from the womb |
|
3 |
Gestation |
Pre-birth |
Total sustenance and support within the womb |
|
|
Conception |
|
Sperm meets egg |
|
1 |
Heritage |
Pre-conception |
The genetic and cultural endowments we inherit |
Table 2: FUNDAMENTAL DEVELOPMENTAL SEQUENCE (FDS) / CHAKRAS
 For
the internal Passages of Psyche, Body, and Spirit, the entire series of
alternating Stages and Transitions is called the Fundamental Developmental
Sequence (FDS). Derived from the Tables of Ken Wilber,[1] the FDS
consists of 38 distinct steps. These steps can be consolidated into 12 developmental
Clusters, – consisting of 12 Stages, separated by 11 Transitions. Step numbers
are shown in the left-hand column; Stages and States are indicated by bands of
color comprising several rows; Transition rows are italicized in grey.
For
the internal Passages of Psyche, Body, and Spirit, the entire series of
alternating Stages and Transitions is called the Fundamental Developmental
Sequence (FDS). Derived from the Tables of Ken Wilber,[1] the FDS
consists of 38 distinct steps. These steps can be consolidated into 12 developmental
Clusters, – consisting of 12 Stages, separated by 11 Transitions. Step numbers
are shown in the left-hand column; Stages and States are indicated by bands of
color comprising several rows; Transition rows are italicized in grey.
Within those 12 Clusters, the seven central Stages are known in Eastern philosophy as the Chakras. From a Western perspective, the Chakras are a consolidation, condensation, or simplification of the FDS into seven basic Stages. From an Eastern perspective, the Chakras are energy phenomena that manifest themselves simultaneously in the three internal Realms of Body, Psyche, and Spirit. The simplified Chakras are shown in the right-hand column (with Wilber’s version in Column 3), using the colors traditionally assigned to each level.
|
FDS Numberp |
FUNDAMENTAL DEVELOPMENTAL SEQUENCE (Wilber) |
Definitions of FDS Terms |
Chakras |
Chakras |
|
38 |
[Beyond consciousness/ Divine] |
[Beyond consciousness] |
|
7. WISDOM (crown of head) |
|
37 |
- transition - |
[Relinquishment of consciousness] |
|
|
|
36 |
Non-dual: Late |
Constant consciousness |
|
|
|
35 |
Non-dual: Middle |
Spirit and World Process |
|
|
|
34 |
Non-dual: Early |
Non-dual mysticism – union of form and formless |
(Release of all Chakras in the Real) |
|
|
33 |
- transition - |
Merging of consciousness with Creator |
|
|
|
32 |
Causal: Late |
Cessation -- union with the source of all manifest realms |
|
|
|
31 |
Causal (formless): Early |
Formless mysticism – awareness of the source of consciousness |
|
|
|
30 |
- transition - |
Emergent consciousness of the holy essence of the Creator |
(Higher Chakras to cessation) |
|
|
29 |
Subtle: Late |
Union with creator of gross realm |
|
|
|
28 |
Subtle (archetype): Early |
Deity mysticism – awareness of divine source of creation |
|
|
|
27 |
- transition - |
Departure from the material realm. Emergent consciousness of the Creator |
7. Sahasrara: Transcendental consciousness, light |
|
|
26 |
Psychic: Late |
Union with the world process |
|
|
|
25 |
Psychic (vision): Early |
Nature mysticism – awareness of divine embodied in the material |
|
|
|
24 |
- transition - |
Emergent consciousness of supernatural realm beyond the material |
6. Psychic
mind: |
|
|
23 |
Vision/ logic: Late |
Integrated
perspectives: |
|
6. VISIONARY THOUGHT (brow, third eye) |
|
22 |
Vision/logic:Middle |
Interacting
perspectives: |
|
|
|
21 |
Vision/ logic: Early |
Multiple
perspectives: |
|
|
|
20 |
- transition - |
Emergence from mechanistic to fluid, multi- dimensional thinking |
5. Verbal-rational mind |
|
|
19 |
Formal: Late |
Broad, complex abstract and logical thinking |
|
5. EXPRESSION (throat) |
|
18 |
Formal: Early |
Small, simple abstract and logical thinking |
|
|
|
17 |
- transition - |
Emergence from myth and superstition to generalized, abstract logical thinking |
4. Community-mind: love |
|
|
16 |
Rule/role: Late |
Large, complex social structures – elaborate rules and roles |
|
4. LOVE (heart) |
|
15 |
Rule/role: Early |
Small, simple social structures – basic rules and roles |
|
|
|
14 |
- transition - |
Emergence of god-centered social structures (rules and roles) and concrete, literal thinking |
|
|
|
13 |
Concept |
Capacity to derive abstract principles from related experiences |
3. Intential-mind: power |
3. POWER (solar plexus) |
|
12 |
Endocept |
Grasping or apprehending the internal, hidden characteristics of an object |
|
|
|
11 |
Symbol |
Capacity to
use signs, characters, objects to represent something else |
|
|
|
10 |
Image |
Capacity to visualize or otherwise experience something not present |
|
2. SEXUALITY (genitals) |
|
9 |
Impulse/ emotion |
Capacity to experience self-centered urges, drives, desires |
2. Emotional-sexual |
|
|
8 |
- transition - |
Emergence of capacity to respond |
|
|
|
7 |
Exocept |
Apprehending the external appearance of an object |
|
1. SURVIVAL (floor of pelvis) |
|
6 |
Perception |
Capacity to receive information from environment through sense organs |
|
|
|
5 |
Sensation |
Capacity to
feel undifferentiated stimulation of sense organs |
|
|
|
4 |
Matter: Molecular, polymer |
Atoms bonded into molecules |
|
|
|
3 |
Matter: Atomic |
Discrete atoms |
1. Material |
|
|
2 |
Matter: Subatomic |
Subatomic
particles |
|
|
|
1 |
[Before matter/ Void] |
[Before creation: Before matter came into existence] |
|

Table 3: PSYCHE PASSAGES
Psyche Passages are the internal phases of mental Maturation that occur as we progress through the Stages of psychological Development. In the simplified schema below, Psyche Passages progress through seven Chakra-related Stages of Maturity (left column), occur within several psychological Arenas (other columns), and focus on particular psychological Issues at each Stage (cells of each column). For a more comprehensive treatment, see Arrays, Tables 4A-I.
|
Chakras |
Central Focus |
Psycho-social |
Ego |
Cognition |
|
Understanding, knowing, transcendence, peace |
Immortality vs extinction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clairvoyance, imagination, psychic experiences, inspiration |
Integrity vs despair Generativity/ |
Post-formal Inter-individual |
Polyvalent logic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Communication, creative expression, synthesis of ideas into symbols/ words |
Intimacy vs isolation Individual identity vs role confusion |
Formal-institutional |
Formal operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. LOVE (heart) |
Relationships, emotions, affinity, compassion, self-acceptance |
Group identity vs alienation Industry vs inferiority |
Interpersonal |
Concrete operations |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
3. POWER (solar plexus) |
Will, purpose, autonomy, identity, self-esteem |
Intiative vs guilt-anxiety |
Imperial |
Intuitive conceptual |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
2. SEXUALITY (genitals) |
Urges, desire, passion, pleasure, feelings |
Autonomy vs shame-doubt |
Impulsive |
Preconceptual |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
1. SURVIVAL (floor of pelvis) |
Grounding, security, stability, trust, vitality physical health |
Trust vs mistrust |
|
Sensorimotor |
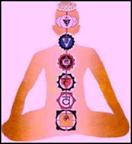
Table 4: BODY PASSAGES
Body Passages are the internal phases of physical Enlivenment that occur as we activate and connect the Energy Centers of our body. In the simplified schema below, Body Passages progress through seven Chakra-related Stages of Functioning (left column), occur within several physical Arenas (other columns), and focus on particular bodily Issues at each Stage (cells of each column).[5] For a more comprehensive treatment, see Arrays, Tables 5.
|
Chakras |
Spine |
Bodily System |
Sensory Mode |
Typical Maladies |
|
7. WISDOM (crown of head) |
Cranium |
Central nervous system |
Clairvoyance |
Alienation, confusion, apathy |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
6. VISIONARY THOUGHT (brow, third eye) |
Upper neck |
Nerves |
Visualization |
Vision problems, headaches, nightmares |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
5. EXPRESSION (throat) |
Lower neck |
Respiration |
Hearing |
Lung and throat problems, thyroid, colds, hearing, asthma |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. LOVE (heart) |
Upper spine |
Circulation |
Touch |
Coronary disease, high/low blood pressure, anemia |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
3. POWER (solar plexus) |
Mid spine |
Digestion |
Sight |
Digestive troubles, ulcers, diabetes |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
2. SEXUALITY (genitals) |
Lower spine |
Reproduction |
Taste |
Sexual problems, menstrual, menopause |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
1. SURVIVAL (floor of pelvis) |
Base spine |
Elimination |
Smell |
Elimination, weight, skeletal problems |

Table 5: SPIRIT PASSAGES
Spirit Passages are the internal phases of spiritual Enlightenment that occur as we ascend through the Stages and States of spiritual Development. In the simplified schema below, Spirit Passages manifest themselves through seven Chakra-related Stages of spiritual Enlightenment (left column), occur within several spiritual Arenas (other columns), and focus on particular spiritual Issues at each Stage (cells of each column). For a more comprehensive treatment, see Arrays, Tables 6A-D.
|
Chakras |
Greek Deities |
Deadly
Sins/ |
Sacraments |
Moral
Span |
|
Zeus |
Pride/
|
Unction (death) |
All earthly beings, natural law |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Athene |
Sloth/
|
Ordination |
All humans |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Anger/
|
Confession (surrendering to divine will) |
Tribe, nation |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. LOVE (heart) |
Envy/
|
Marriage |
Family, clan |
|
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
3. POWER (solar plexus) |
Greed/
|
Confirmation |
Self/mother |
|
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
2. SEXUALITY (genitals) |
Demeter |
Lust/ |
Communion |
Symbiotic |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
1. SURVIVAL (floor of pelvis) |
Poseidon |
Gluttony/ |
Baptism |
Undifferentiated |
[TABLE UNDER DEVELOPMENT]

Table 6: THE CHAKRAS: INTERNAL PASSAGES
From a Western perspective, the Chakras are a consolidation, condensation, or simplification of the FDS into seven basic Stages. From an Eastern perspective, the Chakras are energy phenomena that manifest themselves simultaneously in all three internal Realms of Body, Psyche, and Spirit. In the simplified schema below, the Chakras are shown in the left-hand column, with examples from the three internal Realms in the next three columns. The colors are those traditionally assigned to each Chakra.
|
Chakras |
Psyche Passages |
Body
Passages |
Spirit
Passages |
Seven Dwarfs[9] |
|
Self-transcendence |
Central nervous system |
Prayer |
Happy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Self-actualization |
Nerves |
Contemplation |
Doc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Self-esteem |
Respiration |
Silence, chants |
Sneezy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. LOVE (heart) |
Belongingness/ love |
Circulation |
Seclusion |
Bashful |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
3. POWER (solar plexus) |
Safety/ security |
Digestion |
Renunciation of earthly possessions |
Grumpy |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
2. SEXUALITY (genitals) |
Safety/ security |
Reproduction |
Mortification of the flesh |
Dopey |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
1. SURVIVAL (floor of pelvis) |
Physiological |
Elimination |
Fasting |
Sleepy |
[TABLE UNDER DEVELOPMENT]

Table 7: ARENAS (Life Passages)
Arenas are the spheres of action, the types of experience, the themes of development, or the aspects of personal evolution within each Realm in which growth takes place. Life Passages are the external phases of accomplishment or achievement that occur as we progress through the biologic life cycle. The Realm of Life Passages includes the ten different Arenas shown below.
|
Arena Number |
Arena |
Activities and objectives |
|
|
INDIVIDUAL ARENAS |
|
|
Education & skills-building |
Obtaining the education and training we need to attain our life goals. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Career & calling |
Discovering what work we are meant for, how to succeed in it, and how to adjust to changing work conditions. |
|
|
Finances & investments |
Building and maintaining the financial resources we need to stay comfortable and to achieve our life goals. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Health & well-being |
Maintaining, enhancing, and restoring our health, vitality, and well-being. |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Recreation & enjoyment |
Savoring life to the fullest. Taking pleasure in everything we do. |
|
|
COLLECTIVE ARENAS |
|
|
6 |
Relationships & marriage |
Building intimate relationships that are happy, stable, and mutually supportive. Finding the right life partner. |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Sexuality & sensuality |
Developing a sexual relationship with a beloved partner that is intimate, meaningful, and satisfying. Enjoying the world around us as a pleasure-filled, sensory experience. |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Family & children |
Birthing and raising children who are happy, healthy, well-adjusted, caring, creative, responsible, and successful. |
|
|
|
|
|
Friendships & community |
Developing deep, lasting friendships with kindred spirits. Contributing to the strength and vigor of our communities. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Society & culture |
Supporting and building our society. Catalyzing the evolution of our culture. |
|

Table 8: ISSUES OF THE RELATIONSHIP ARENA
(Life Passages)
At each Stage of life, and within each Arena, we grow by encountering certain key Issues. These challenging Issues must be addressed and resolved to transition successfully to the next Stage. In the Arena of Relationships and Marriage, we build intimate relationships that are happy, stable, and mutually supportive -- and seek to find the right life partner. In this Arena the following Issues may assume major importance.
|
Age of |
Relationship situations |
Typical issues |
||
|
25 |
Legacy |
Influence on descendents |
Passing along a lifetime of wisdom and experience. Adding to family and cultural traditions. |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Loss of partner |
Mourning and recovering from loss of loved one. |
|||
|
Partners support and assist |
Supporting one another in compassion and trust. |
|||
|
Relationship rejuvenates |
Restoring passion and intimacy to the relationship. |
|||
|
Relationship stabilizes |
Remaining close while growing. Resolving differences and conflicts maturely. |
|||
|
Long-term partnership |
Building solid, authentic lifelong relationship based on meaningful shared values. |
|||
|
13 |
Adolescence |
Temporary partnerships |
Experimentation and experiencing relationships. |
|
|
11 |
Older childhood |
Friends, schoolmates |
Building friendships. Acculturation. |
|
|
9 |
Young childhood |
Bonding with father |
Degree and quality of paternal attentiveness. Detachment, domination, abuse. |
|
|
7 |
Toddler |
Semi-independence from mother |
Over-protectiveness or inattention. |
|
|
5 |
Infancy |
Bonding with mother |
Quality and availability of attention. Maternal neglect or unresponsiveness. |
|
|
3 |
Gestation |
Union with mother |
Uterine environment – nourishment and toxicity. Maternal moods. |
|
|
1 |
Heritage |
Influence of ancestors |
Family cultural and religious traditions. Patterns of connection or abuse. |

Table 9: ENNEAGRAM ROLES
The Persona (or Role) is our ‘public face’ -- the set of attributes and behaviors we construct to enable the Self to play a part in the drama of existence. The Enneagram is a particular system for categorizing (‘typing’) Personae. An Enneagram Role (‘Enneagram Type’) is the fundamental cluster of attributes by which the Self manifests its public character. According to Enneagram theory, every person exhibits one of nine dominant Roles. Each Role is endowed with Traits that can become fixated, or can evolve as the person grows.
|
Enneagram number |
Enneagram Role[10] |
Characteristics |
Fixated Traits |
Evolved Traits |
|
1 |
Reformer |
Principled, idealistic |
Rigid, judgmental |
Idealistic, visionary |
|
2 |
Helper |
Caring, self-sacrificing |
Possessive, manipulative |
Generous, compassionate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Achiever |
Ambitious, adaptive |
Driven, boastful |
Pragmatic, high-achieving |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Individualist |
Romantic, introspective |
Withdrawn, self-absorbed |
Passionate, creative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Investigator |
Intense, cerebral analysts |
Isolated, preoccupied |
Perceptive, innovative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Loyalist |
Committed, security-oriented team-players |
Suspicious, conformist |
Responsible, faithful |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Enthusiast |
Busy, social bon-vivants |
Scattered, escapist |
Gregarious, optimistic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Challenger |
Powerful, dominating |
Domineering, tactless |
Self-confident, decisive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
Peacemaker |
Good-natured, easy-going, conciliators |
Passive, self-effacing |
Inclusive, serene |

Table 10: CULTURE PASSAGES
Culture Passages are the internal (cultural) and external (societal) phases of development that occur as mass populations progress through the Stages of cultural growth. In the simplified schema below, Culture Passages progress through seven Chakra-related Stages of Development (column 1) -- following a growth path similar to individuals, but spread over eons of time (column 2). The Spiral Dynamics[11] model (column 4) is perhaps the most popular and influential contemporary system of Culture Passages. In any present-day culture, vestiges of all previous cultural Stages are still to be found (column 5). For a more comprehensive treatment, see Arrays, Table 6A-D.
|
Chakras |
Ascendance |
Cultural stages |
Spiral
Dynamics |
Cultural
layers |
|
7. WISDOM (crown of head) |
[2000+ AD?] |
[Harmonious civilization orchestrated by Holy Spirit] |
[next awakening] (coral) Holistic organism/ global (turquoise) |
Translucents, intelligent design, vibrational medicine, saints Cultural creatives, integral psychology, Bioneers, Esalen, Gaia |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
6. VISIONARY THOUGHT (brow, third eye) |
1950 AD |
Global economies coordinated by networks |
Systematic process/ integrative (yellow)
Social network/ Relativistic (green) |
Ecology, appropriate technology, biomimicry, permaculture Co-ops, Peace Corps, sensitivity training, affirmative action, idealistic crusaders, Olympic Village Silicon Valley, dot-com entrepreneurs, software programmers |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
5. EXPRESSION (throat) |
1500 AD |
Mercantile nations run by machines |
Strategic enterprise/ Individualistic-achiever (orange) |
Multi-national corporations, Wall Street, bureaucrats, assembly-line workers, foot soldiers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. LOVE (heart) |
4000 BC |
Agrarian empires ruled by dominant god |
Authority/ Absolutist-religious (blue) |
Family farmers, Amish communities, Boy Scouts, orthodox Jews, 12-Step members |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
3. POWER (solar plexus) |
20,000 BC |
Militaristic hordes driven by pagan gods |
Strong-man/ Power-gods (red) |
NFL teams, neo-Nazis, Black Panthers, Mafia clans |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
2. SEXUALITY (genitals) |
50,000 BC |
Nomadic kinship clans controlled by spirits |
Tribe/ Magical-animistic (purple) |
Street gangs, Star Trek groupies, Masonic lodges, herbalists |
|
- transition - |
|
|
|
|
|
1. SURVIVAL (floor of pelvis) |
Dawn of humanity |
Hunting bands united for survival |
Survival band/ Instinctive (beige) |
Mountain climbers, cowboys, street people, terrorists, Rambo |

Table 11: GENERATIONAL CYCLES[12]
A Generation is the biological period of life, normally about 20-25 years, between the time one is born and the time one first procreates. The Generational Cycle is a series of four characteristic Generations – Prophetic, Reactive, Civic, Bureaucratic – which dynamic cultures repeatedly pass through. The Table below outlines the five Generational Cycles that have occurred in America since it was first colonized. For each Generation, the range of possible birth dates is shown, along with prominent members who were born during that period.
|
Generation number |
Generation Cycle |
Prophetic |
Reactive |
Civic |
Bureaucratic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Translucent? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Vision-logic? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Millenial |
Boomer |
X-Gen |
Millenial |
Protected? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Great Powers |
Missionary |
Lost |
G. I. |
Silent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Civil War |
Transcendental |
Gilded |
[Aborted by mass slaughter] |
Progressive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
Revolutionary |
Awakening |
Liberty |
Republican |
Compromise |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Colonial |
Puritan |
Cavalier |
Glorious |
Enlightenment |
|
|
 Appendix B:
Appendix B:
RESOURCES FOR STUDY
There is a growing body of literature describing and explaining every aspect of the Growth Continuum. An essential library might include the following.[13]
Ken Wilber/ Integral Studies
One of the most insightful and comprehensive thinkers of our time. Hip and accessible. A major inspiration for this study.
{ Wilber, Ken: Works. Especially pertinent to this study:
* Integral Psychology – Consciousness, Spirit, Psychology, Therapy (IP). Boston, MA (2000): Shambala Publications.
* Transformations of Consciousness: Conventional and Contemplative Perspectives on Development . Boston, MA (1973, 1986): Shambala Publications.
* Integral Spirituality: A Startling New Role of Religion in the Modern World. Boston, MA (2006): Shambala Publications.
* A Brief History of Everything. Boston, MA (1996, 2000): Shambala Publications.
* Up From Eden: A Transpersonal View of Human Evolution. Garden City, NY (1981): Anchor Press/Doubleday.
{
Visser, Frank 2003. Ken Wilber – Thought as
Passion. Albany, NY: SUNY Press.
Excellent and readable guide to Wilber’s life and work.
{
Reynolds, Brad 2004. Embracing Reality – The
Integral Vision of Ken Wilber. New York, NY: Tarcher/ Penguin.
Thorough and faithful summaries of Wilber’s works.
{ Martin, Hugh and Kaye 2007. Arrays of Light: Ken Wilber’s Tables of Correspondence (‘Arrays’). IntegralWorld.net. In preparation as of April 2007: The Processes of Growth (‘Processes’); and, The Processes in Real Life (‘Real Life’).
Life Passages
{
Sheehy, Gail 1995. New Passages – Mapping Your
Life Across Time. New York, NY: Random House. (Life, Culture, Participants)
The reigning queen of Life Passage studies.
Psyche Passages
{
Erikson, Erik 1950. Childhood and Society. New
York, NY: Norton. (Life, Psyche, Culture)
Classic psychoanalytic study on the development of character.
{
Maslow, Abraham H. 1968. Toward a Psychology of
Being. New York, NY: Wiley (Life, Psyche)
Famous and influential exploration of the hierarchy of human needs. (Psyche,
Life)
{
Piaget, Jean and Barbel Inhelder 1958. The
Growth of Logical Thinking from Childhood to Adolescence: An Essay on the
Construction of Formal Operational Structures. New York, NY: Basic Books.
The classic research on the development of logical intelligence. (Psyche –
Cognitive)
Body Passages
{
Easley, Norman 2006. Naturopathic Medicine.
Santa Rosa, CA: Unpublished manuscript. (Chakras, Body)
The most thoroughly-investigated study of the connection between bodily
processes and psycho-spiritual health.
Spirit Passages
{ Wilber, Ken (2006). See above.
{
Myss, Caroline 1996. Anatomy of the Spirit: The
Seven Stages of Power and Healing. New York, NY: Harmony Books. (Spirit,
Psyche)
Sensitive exploration of the spiritual energy centers from the perspective of
Christian sacraments and the Hebrew Kaballah.
Culture Passages
{
Beck, Don Edward & Christopher C. Cowan
1996. Spiral Dynamics – Mastering Values, Leadership, and Change. Malden, MA:
Blackwell Publishing. (Culture)
Sophisticated and illuminating explication of Culture Passages and
developmental levels in general.
{
Howe, Neil and William Strauss 1991. Generations
– The History of America’s Future, 1584 to 2069. New York, NY: Wm. Morrow.
(Culture, Generations)
Masterwork on the four-stage cycle by which cultures evolve.
{
Ray, Paul H. and Sherry Ruth Anderson 2000. The
Cultural Creatives – How 50 Million People Are Changing the World. New York,
NY: Harmony/Random House. (Psyche, Culture)
Valuable survey of the exciting psychological transformation at work in today’s
culture.
Internal Passages & Chakras
{
Judith, Anodea 1996. Eastern Body, Western Mind
– Psychology and the Chakra System. Berkeley, CA: Celestial Arts. (Internal
Passages, Chakras, Participants)
Comprehensive and insightful exposition of the Chakras at all three levels.
Participants
{
Riso, Don Richard & Russ Hudson 1999. The
Wisdom of the Enneagram – The Complete Guide to Psychological and Spiritual
Growth for the Nine Personality Types (Roles). New York, NY: Bantam
Books. (Roles, Enneagram)
Clearest discussion of the Enneagram types and their potential for personal
evolution.
{
Kegan, Robert 1982. The Evolving Self –
Problem and Process in Human Development. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University
Press (Self).
Landmark work on human development from a Western academic perspective.
{
Rowan, John 1990. Subpersonalities – the People
Inside Us. New York, NY: Routledge. (Subpersonalities, Impediments)
Intriguing study of the characters and demons that populate our interiors.

Appendix C:
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
This Table displays all the key terms and concepts pertaining to the Growth Continuum. Each term is defined and its first appearance in the text noted. The closest equivalent in Ken Wilber’s AQAL system is indicated in column 4. Further information on the nature and degree of correspondence (or divergence) is footnoted in the main text. In the main text, these terms are Capitalized; the first appearance of each term is bolded.
|
Term |
Definition |
First |
Wilber equivalent (closest) |
|
Arenas |
The spheres of action, the realms of experience, the themes of development, or the aspects of personal evolution within each Realm in which growth takes place |
10 |
Lines |
|
Body Passages |
The internal phases of physical Enlivenment that occur as we awaken and connect the Energy Centers of our body |
9 |
|
|
Bonding |
Our connection to others. Our identification with a particular Stage |
16 |
|
|
Bureaucratic generation |
The Generation that institutionalizes and standardizes what once was the Prophetic Vision. Phase 4 of the Generational Cycle. |
14 |
|
|
Chakras |
Energy phenomena that manifest themselves simultaneously in all three internal Realms of Body, Psyche, and Spirit |
9 |
Same |
|
Civic generation |
The Generation that fills out and implements the vision of the Prophetic Generation. Phase 3 of the Generational Cycle. |
14 |
|
|
Collective |
Group Participants in the growth process |
11 |
|
|
Collective Participants |
Every human group from two-person relationships, to families, to workgroups, to communities, to cultures |
13 |
|
|
Contributing Roles |
Supporting Enneagram Role |
12 |
|
|
Coordination |
Combining all Dimensions of growth into balanced, harmonious whole |
18 |
|
|
Culture Passages |
Follow a Stage-related growth path similar to individuals, but spread over vast eons of time |
13 |
|
|
Differentiation |
The Self transcends a particular Stage by dis-identifying with it |
7 |
Same |
|
Dimensions |
The eight facets or types of growth in the Growth Continuum |
5 |
|
|
Directions |
Internal growth in psyche, body, and spirit takes place in two opposite Directions – ascending and descending |
15 |
Evolution and involution |
|
Disattachment |
Failing to establish a solid bond or commitment to a new Stage – thereby remaining alienated, fragmented, rootless, homeless, in limbo. Opposite of Re-identification. |
16 |
Same |
|
Dissociation |
Avoiding, denying, repressing, or disowning the Observed Self. Opposite of Integration. |
16 |
Same |
|
Dominant Role |
Primary Enneagram Role |
12 |
|
|
Enneagram |
A system for categorizing (‘typing’) Personae |
12 |
|
|
Enneagram Role |
The fundamental cluster of attributes by which the Self manifests its public character |
12 |
Enneagram type |
|
Experienced Self |
I-Self. The observing, subjective, inside Self. Identifies with our current Stage of development |
11 |
Proximate Self, self-sense |
|
Fixation |
Clinging to an old Stage, failing to Differentiate – remaining fixated, fused, embedded, arrested. Opposite of Differentiation. |
16 |
Same |
|
Fundamental Developmental Sequence |
The entire series of alternating Stages and Transitions |
7 |
Correlative structure |
|
Generation |
A biological period of life, normally about 20-25 years, between the time one is born and the time one first procreates. |
14 |
|
|
Generational cycle |
A series of four Generations that occurs repeatedly in the growth of dynamic Cultures |
14 |
|
|
Generational growth |
A form of Collective Growth that occurs from one Generation to the next, and from one Generational Cycle to the next |
14 |
|
|
Gremlins |
Pernicious or malevolent Sub-personalities spawned when the Self fails to dis-identify with a past stage. Also called inner saboteurs or shadow-selves. |
13 |
|
|
Growth continuum |
A field of growth consisting of eight interwoven Dimensions |
5 |
|
|
Identification |
The Self identifies with a particular Stage of development |
7 |
Same |
|
Immediate Self |
Experienced and Observed Selves together |
11 |
Overall Self |
|
Impediments |
Problems -- all the ways the growth process can go wrong |
16 |
Pathologies |
|
Individual |
Single Participant in the growth process |
11 |
|
|
Integration |
The Self consolidates the new identification -- integrating the new Experienced Self with the old Observed Self |
7 |
Same |
|
Inter-passage growth |
The trajectory the Self passes through -- from internal, to external, and back to internal |
12 |
U-shaped pattern of development, Pre-/Trans- Fallacy |
|
I-Self |
See Experienced Self |
11 |
Same |
|
Life Passages |
The external phases of accomplishment or Achievement that occur as we progress through the Life Cycle |
8 |
Horizontal translation |
|
Me-Self |
See Observed Self |
11 |
Same |
|
Observed Self |
Me-Self. The detached, objective, outside Self. The Self from a prior Stage of development that we have transcended, or ceased to identify with |
11 |
Distal Self, self-system |
|
Overall Self |
The Immediate and Transcendent selves together |
11 |
|
|
Passages |
The four major sequences of human growth corresponding to the four Realms |
8 |
|
|
Persona |
Our ‘public face’ -- the set of attributes and behaviors we construct to allow the Self to play a part in the drama of existence |
12 |
Membership-Self, Rule/Role region |
|
Polarities |
The fundamental extremes of the universe – male and female, mind and body, spirit and flesh, symbol and meaning, yang and yin |
14 |
|
|
Processes |
All the techniques, therapies, practices, programs, activities, explorations, studies, and focused experiences that move us along the Growth Continuum |
5 |
|
|
Prophetic generation |
The Generation that conceives a new cultural vision and a new impetus for change. Phase 1 of the Generational Cycle. |
14 |
|
|
Psyche Passages |
The internal phases of mental Maturation that occur as we progress through the Stages of psychological Development |
9 |
Vertical transformation |
|
Reactive generation |
The Generation that reacts against or detaches from the dominance of the Prophetic Generation. Phase 2 of the Generational Cycle. |
14 |
|
|
Realms |
The major domains or spheres of human experience in which growth and development can occur |
8 |
Realms, planes, domains, spheres, and axes |
|
Re-identification |
The Self begins to identify with the subsequent Stage of development |
7 |
|
|
Role |
See Persona |
12 |
|
|
Self |
Individual Participant in the growth process. Encountered in three aspects: Experienced, Observed, and Transcendent Self. |
11 |
Same |
|
Spiral Dynamics |
The most popular and influential contemporary system of Culture Passages |
14 |
Same |
|
Spirit Passages |
The internal phases of spiritual Awakening that occur as we ascend through the Stages and States of spiritual Development |
9 |
Vertical transformation |
|
Stage Growth |
Occurs as we meet and master the challenges presented by a particular Stage |
6 |
|
|
Stages |
The levels of development, maturity, enlivenment, or enlightenment through which we pass as we grow |
6 |
Stages, levels, waves, spheres, nests, holistic patterns |
|
States |
The four levels of spiritual experience: Nature mysticism (psychic), deity mysticism (subtle), formless mysticism (causal), and non-dual mysticism |
9 |
Same |
|
Sub-personalities |
Benign or pernicious mini-identities that emerge in response to specific life situations |
13 |
Same |
|
Transcendent Self |
The Witness. The all-pervasive Seer or I-I-Self. Our Essence, True Self, or True Nature |
11 |
Witness, ultimate subject, pure consciousness, antecedent self, emptiness |
|
Transformation |
Times when we are becoming something we have never been before |
6 |
Same |
|
Transition Cycle |
The four-phase process through which Transition takes place |
6 |
Fulcrum, milestone, round |
|
Transitions |
The quantum leaps that take us from one Stage to the next |
6 |
|
|
Translation |
Times when we are becoming better at activities we already know how to do |
6 |
Same |
|
Vectors |
The four major Quadrants of reality along which human growth proceeds – combining the Individual and Collective Participants with the inner and outer Passages of growth |
14 |
Quadrants |
|
Witness |
See Transcendent Self |
11 |
|
Appendix D:
CREDITS
Thanks is gratefully given for permission to publish the following images.
Title page. GrowthRoots. UKansas.edu.
Stage growth. DNA Flow, Genomenewsnetwork.org
Transition growth. Bay Bridge at Night, Thomashawk.com
Realm growth. Realms of Humanity, Arrowriver.ca
Arena growth. Coliseum by Moonlight, Hillmanwonders.com
Participant growth. Whitewater. Oxeyes.org.uk.
Vector and direction growth. Red Arrows in Formation, Bluelinecruises.co.uk
Therapeutic growth. Personalities, WebRing.com
Coordination growth. Gymnast, Photosport.com
Tables:
1. Stages of Human Development, W. H. Freeman.
2. DNA Spiral, www.berkeley.edu
3. Soul, SusanArt.org
4. Chakras in the Etheric Body, Shivayoga.net
5. A Journey Beyond – Passing Barnard’s Star, NewTox.com.
6. RealmKeepers, Photobucket.com
7. Gladiator, Dreamworks Studios
8. The Wedding 2, Ezthemes.com
9. Parthenon, Macalester College, Classics Department, Macalester.edu.
10. Laurel and Hardy, Way Out West, Hal Roach Studios.
11. Norman Rockwell, Freedom From Want, ArtArchive.com
Resources. Big Book, Sterin.com
Glossary. Mag Glass, Nyu.edu
HUGH AND KAYE MARTIN:
Biographical Information

 HUGH
MARTIN is listed in Who’s Who in the World. He has
appeared on numerous talk shows, led seminars at many colleges and
corporations, and spoken at numerous professional conferences and colloquia.
Mr. Martin is president of the NASD-registered securities brokerage firm, Hugh
Martin Securities, and of the SEC-registered investment advisory firm, Hugh
Martin & Co. Hugh is also president and co-founder of the life planning
and counseling firm, Whole Life Advisory.
HUGH
MARTIN is listed in Who’s Who in the World. He has
appeared on numerous talk shows, led seminars at many colleges and
corporations, and spoken at numerous professional conferences and colloquia.
Mr. Martin is president of the NASD-registered securities brokerage firm, Hugh
Martin Securities, and of the SEC-registered investment advisory firm, Hugh
Martin & Co. Hugh is also president and co-founder of the life planning
and counseling firm, Whole Life Advisory.
AMALIA KAYE MARTIN (‘Kaye’) is a gifted natural medicine practitioner and an instructor in nutrition and natural medicine at Baumann College. Kaye is a dedicated homemaker, a devoted mother, perceptive life coach, certified natural foods chef, and dynamic community organizer.
HUGH AND KAYE. Hugh and Kaye are best qualified as integral theorists and practitioners because they have lead integral lives. Both have richly diverse backgrounds in a multitude of fields:
Ø Personal transformation: Esalen, group process, gestalt, Reichian, bioenergetics, Rolfing, yoga, various religious and spiritual traditions.
Ø Natural medicine and health: Homeopathy, chiropractic, acupuncture, organic nutrition, vibrational medicine. Terminal cancer survivor (Hugh). Expert practitioner in nutrition and natural medicine (Kaye)
Ø Artistic and creative expression: Nature photographer, documentary videographer, poet, painter/sculptor (Hugh). Batik artist, home decorator (Kaye).
Ø Education: Ghetto school teacher, college literature instructor, financial seminar leader, early-reading curriculum developer (Hugh). Nutrition/natural medicine instructor, home-school network developer and coordinator (Kaye).
Ø Societal change: Civil rights, environmental issues, sustainability/permaculture.
Ø Natural and cultural environments: Backpacking, mountain biking, exotic travel, home exchanging.
Ø Academics: Hugh -- Swarthmore College
(Bachelor’s), University of Pennsylvania (Master’s), Indiana University (doctoral),
UC Berkeley (credential), Coaches Training Institute (CTI), member of Mensa.
Kaye -- Cal State Northridge (Bachelor’s), Baumann College (natural medicine),
Coaches Training Institute (CTI).
Ø Marriage and family. Thirty years of happy, occasionally turbulent, marriage. Five highly-independent, multi-gifted kids with close family ties.
WHOLE LIFE ADVISORY. Using the experiences and expertise described above, Hugh and Kaye have developed a program of personal and professional growth called Whole Life Advisory. Whole Life Advisory empowers clients to achieve success and fulfillment in the 12 most important arenas of life: education, career, marriage, family, community, emotions, sexuality, finances, health, recreation, nature, and spirituality.
REFERENCES
[1] See Wilber (2000), pp, 197-217 and Arrays.
[2] See Erikson (1950).
[3] See Kegan (1982).
[4] See Piaget (1958).
[5] See Judith (1996) and Easley (1987).
[6] See Myss (1996).
[7] See Arrays, Table 4H2.
[8] See Maslow (1968, 1983).
[9] Just checking that you’re still paying attention!
[10] Role names and characteristics derived in large part from Riso/Hudson (1999).
[11] See Beck (1996).
[12] For further details, see Strauss and Howe (1991).
[13] Items within categories listed roughly in order of importance to this study. Other pertinent Resource categories shown in parentheses.